Arum Palaestinum-derived extracellular vesicles as antibacterial agents against ESKAPE pathogens
Authors: Ahmad Kadriya, Zenab Ali Saleh, Karolina Bierowiec, Wolfgang Eisenreich, Mizied Falah
Ger. J. Microbiol.
2024.
vol. 3, Iss. 3
pp:16-19
Doi: https://doi.org/10.51585/gjm.2024.3.0027
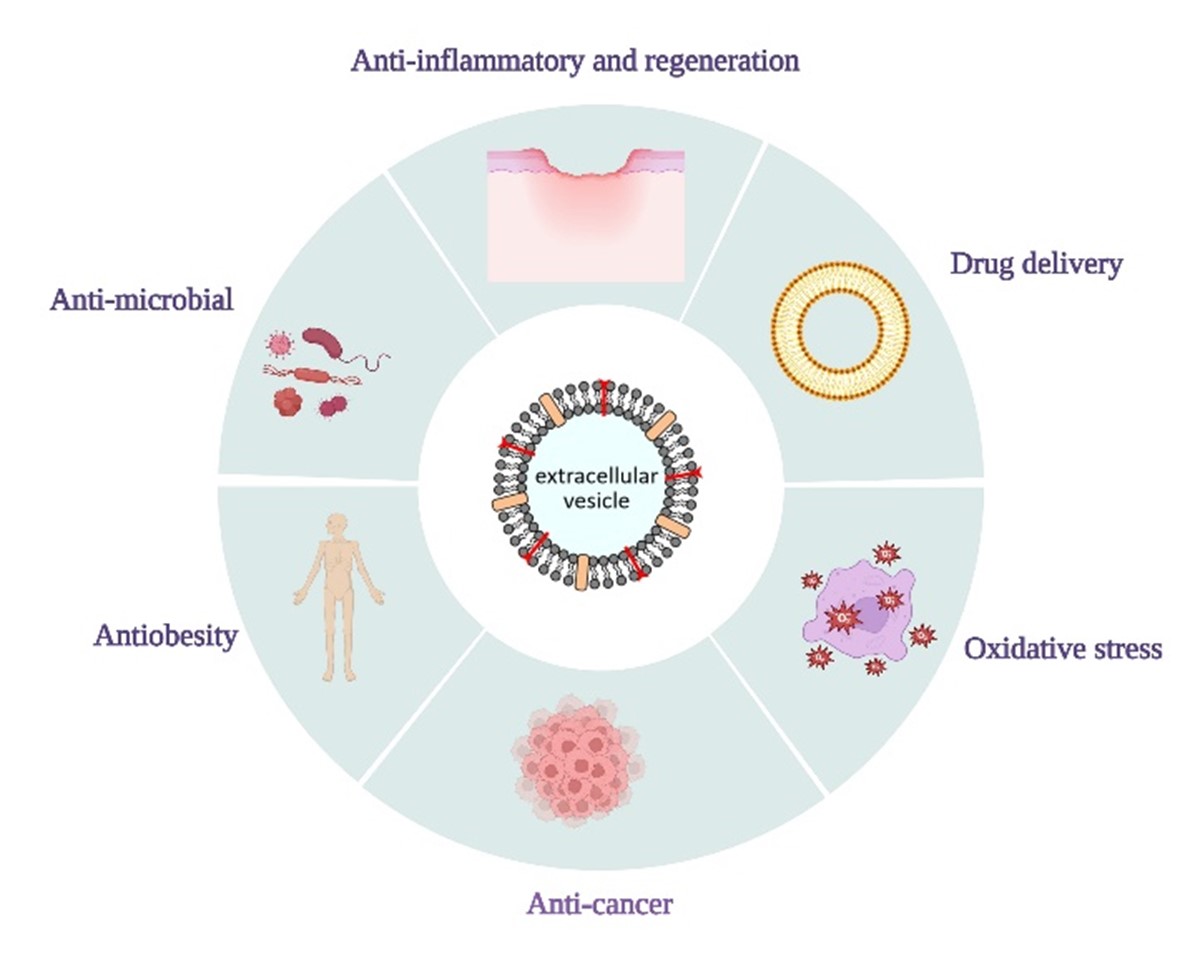
Abstract:
Plant phytosomes are tiny extracellular vesicles (EVs) that transport various molecules, facilitating communication both within and between cells. They can be found in different parts of plants and contain mir-RNA, m-RNA, DNA, lipids, proteins, and metabolites. These vesicles may play a critical role in plant immune response to microbial infections. EVs exert several biological activities, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antiobesity, and anticancer effects. Recently, EVs have been used as a vehicle for drug delivery. Our recent preliminary data has identified antimicrobial effects of Oleaceae-derived EVs against multidrug-resistant bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus, Enterococcus faecalis, and Klebsiella pneumoniae. This letter seeks scientists interested in studying the antimicrobial effects of EVs or their use in drug delivery using natural products against multi-drug resistance.
Keywords:
Arum Palaestinum, Antibacterial agents, Extracellular vesicles, ESKAPE
Statistics:
Article Views: 220
PDF Download: 32