Tracking the diversity and Mediterranean lineage of Brucella melitensis isolates from different animal species in Turkey using MLVA-16 genotyping
Authors: Kadir Akar, Farah Tatar, Gernot Schmoock, Gamal Wareth, Heinrich Neubauer and Osman Erganiş
Ger. J. Vet. Res
2022.
vol. 2, Iss. 1
pp:25-30
Doi: https://doi.org/10.51585/gjvr.2022.1.0037
Abstract:
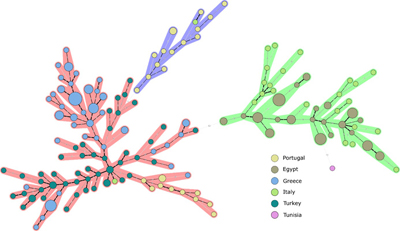
Brucellosis is a zoonotic disease with a high prevalence in humans and farm animals in Turkey. However, data on the genetic diversity of Brucella spp. circulating in Turkey and parts of the Mediterranean region are limited. In the present study, the genetic diversity of 50 B. melitensis isolates from seven regions of Turkey was investigated using multi-locus variable number tandem repeats analysis (MLVA-16). The profiles were compared with 163 B. melitensis isolates recovered from the Mediterranean basin. B. melitensis strains from Turkey contain 46 different genotypes and consist of two main clusters. B. melitensis isolates from Turkey were closely related to isolates from Greece and some Portuguese strains. The same genotypes isolated from different sites show the spread between sites. Therefore, uncontrolled animal movements and the trade of imported animals can be important factors for the spread of brucellosis. The endemic occurrence of B. melitensis in the Mediterranean basin is a result of socio-historical links between Mediterranean countries. Turkish strains belong to the Eastern Mediterranean line. Eradicating brucellosis in countries of the Mediterranean basin with high prevalence is a demanding need to reduce trade barriers and, more importantly, prevent human suffering
Keywords:
Brucella melitensis, Mediterranean basin, Turkey, Genotyping; MLVA-16
Statistics:
Article Views: 2159
PDF Download: 75