Incidence of lumpy skin disease virus with its characterization in vaccinated pregnant Holstein cows in Dakahlia governorate, Egypt
Authors: Samah M. Mosada, Nesma Rasheed, Hanaa S. Ali, Khaled A. S. El-Khabaz, Eman A. M. Shosha and Mohamed El-Diasty
Ger. J. Vet. Res
2021.
vol. 1, Iss. 4
pp:23-33
Doi: https://doi.org/10.51585/gjvr.2021.4.0027
Abstract:
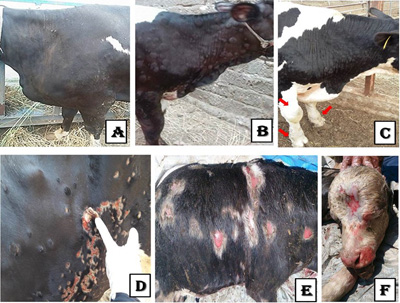
Lumpy skin disease (LSD) is an infectious, economically important viral disease of cattle. Lumpy skin disease virus (LSDV) is still circulating in Egypt, despite the annual mass vaccination with the sheep pox virus vaccine recommended by the Egyptian authorities. This study was carried out on two farms of pregnant Holstein cows vaccinated with Bovivax LSD-N® vaccine (Neethling strain) (farm I) and Servac Capri-C® vaccine (live attenuated sheep pox) (farm II). After 40-60 days post-vaccination, mild clinical signs were detected in 3% of cows on farm I, whereas a more severe clinical infection was developed in 40% of cows on farm II. LSDV was isolated on the chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) of 11-day-old embryonated chicken eggs (ECEs) and Madin Darby bovine kidney (MDBK) cell culture. LSDV was identified in collected skin tissues by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and histopathological examination. Finally, LSDV was confirmed by amplification of 192 base pairs (bp) of the P32 gene using polymerase chain reaction (PCR), and two samples were selected for DNA sequencing. LSDV developed characteristic pock lesions on the CAM of the inoculated ECEs. MDBK cell culture developed a prominent LSDV cytopathic effect at the 3rd passage. Viral particles were detected in the cytoplasm of both epidermal cells and dermal macrophages by TEM. Histopathological examination revealed different lesions correlated with LSDV infection age. LSDV was confirmed in all tested samples by PCR. Our strains (Dakahlia-2020-1 and Dakahlia-2020-2) were closely related to other Egyptian LSDV strains in the GenBank with 98.2-100% identity. The present study proved conclusive evidence that the live attenuated sheep poxvirus vaccine poorly protects Egyptian cattle against LSDV, while the LSDV Neethling strain vaccine gave a promising and sufficient protection rate.
Keywords:
LSDV, Neethling, Sheep poxvirus vaccine, RT-PCR, Phylogenic analysis
Statistics:
Article Views: 2981
PDF Download: 64