Comparative analysis of commercial recombinant vaccination strategies against Newcastle disease in broilers
Authors: Hanan M. F. Abdien, Mohsen M. Z. El-Dimerdash, Eslam A. Morsy, Norhan M. Ali, and Mona S. Abdallah
Ger. J. Vet. Res
2025.
vol. 5, Iss. 1
pp:17-29
Doi: https://doi.org/10.51585/gjvr.2025.1.0116
Abstract:
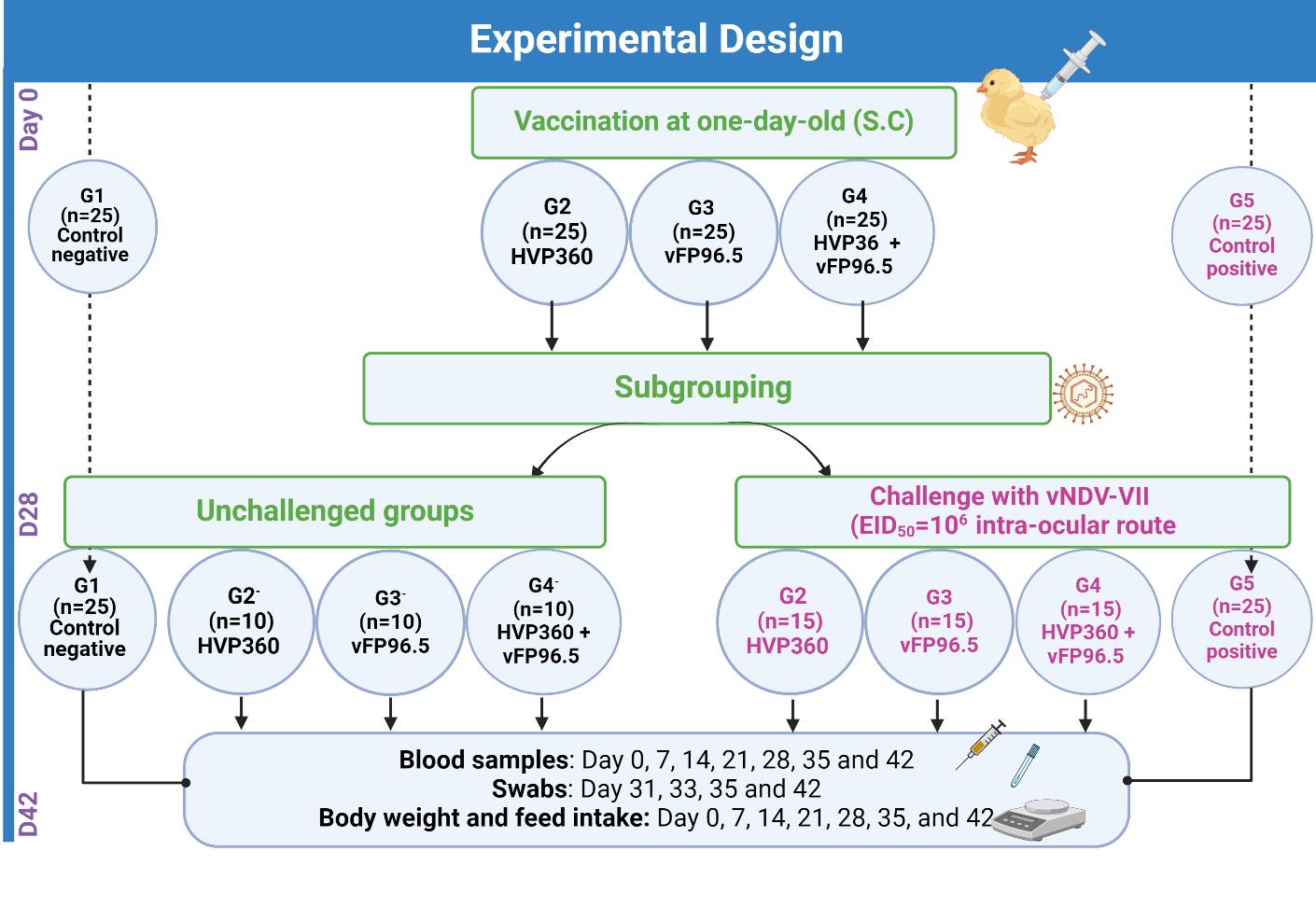
The widespread Newcastle disease (ND) genotype VII among vaccinated and unvaccinated chicken populations makes it one of the most threatening viruses impacting poultry, causing significant losses in the poultry industry. Recently, recombinant vector vaccine technology has proven to induce a durable protective immune response, even in the presence of maternal antibodies, thereby addressing the limitations associated with traditional vaccines. This study evaluated the protective efficacy of the recombinant turkey herpesvirus double construct vaccine (HVP360) that encodes both the NDV-F and IBDV VP2 genes alongside the recombinant fowl pox-based NDV vaccine (vFP96.5) and their combined use against virulent NDV genotype VII. For this purpose, 125 one-day-old broiler chicks (Cobb) were divided into five groups (G1-G5), in which chickens kept in G1 were unvaccinated unchallenged. Chickens kept in G2, G3, and G4 were vaccinated subcutaneously at one day old with HVP360, vFP96, and HVP360+vFP96, respectively. At 28 days of age, half of the birds (n=15) in each vaccinated group (G2, G3, and G4) and the G5 (positive control group) were challenged intraocularly with 106 EID50 velogenic NDV genotype VII. Protection was assessed based on mortalities, clinical signs, seroconversion, and viral shedding. Results demonstrated significant protection offered by the recombinant vaccines, reaching a remarkable level of 93.33% for G2 and G4, followed by 71.42% for G3, associated with a notable reduction of clinical signs and lesions. In contrast, the mortality rate reached 75% in unvaccinated challenged G5. Significant differences in seroconversion based on the hemagglutination (HI) test and ELISA were observed among vaccinated groups on days 14, 21, and 35, in which chickens kept in G3 exhibited the highest antibody titers, followed by G4 and G2. Viral shedding was significantly reduced in all vaccination groups at 3, 5, and 7 days post-challenge, with the highest reduction in dual-vaccinated chickens (G4) followed by G2. In conclusion, the concurrent application of HVP360 and vFP96.5 in combating the ND virus can establish a foundational basis for the vaccination program aimed at one-day-old chicks.
Keywords:
Newcastle disease, Recombinant vaccine, HVP 360, FP96.5
Statistics:
Article Views: 626
PDF Download: 39